Adhesive wear regimes on rough surfaces and interaction of micro-contacts
S. Pham-Ba & J.-F. Molinari
Tribology Letters
Published 22 July 2021
Selected as Best from STLE’s Research Community (Tribology & Lubrication Technology magazine, Nov. 2021)
See full text (at publisher)
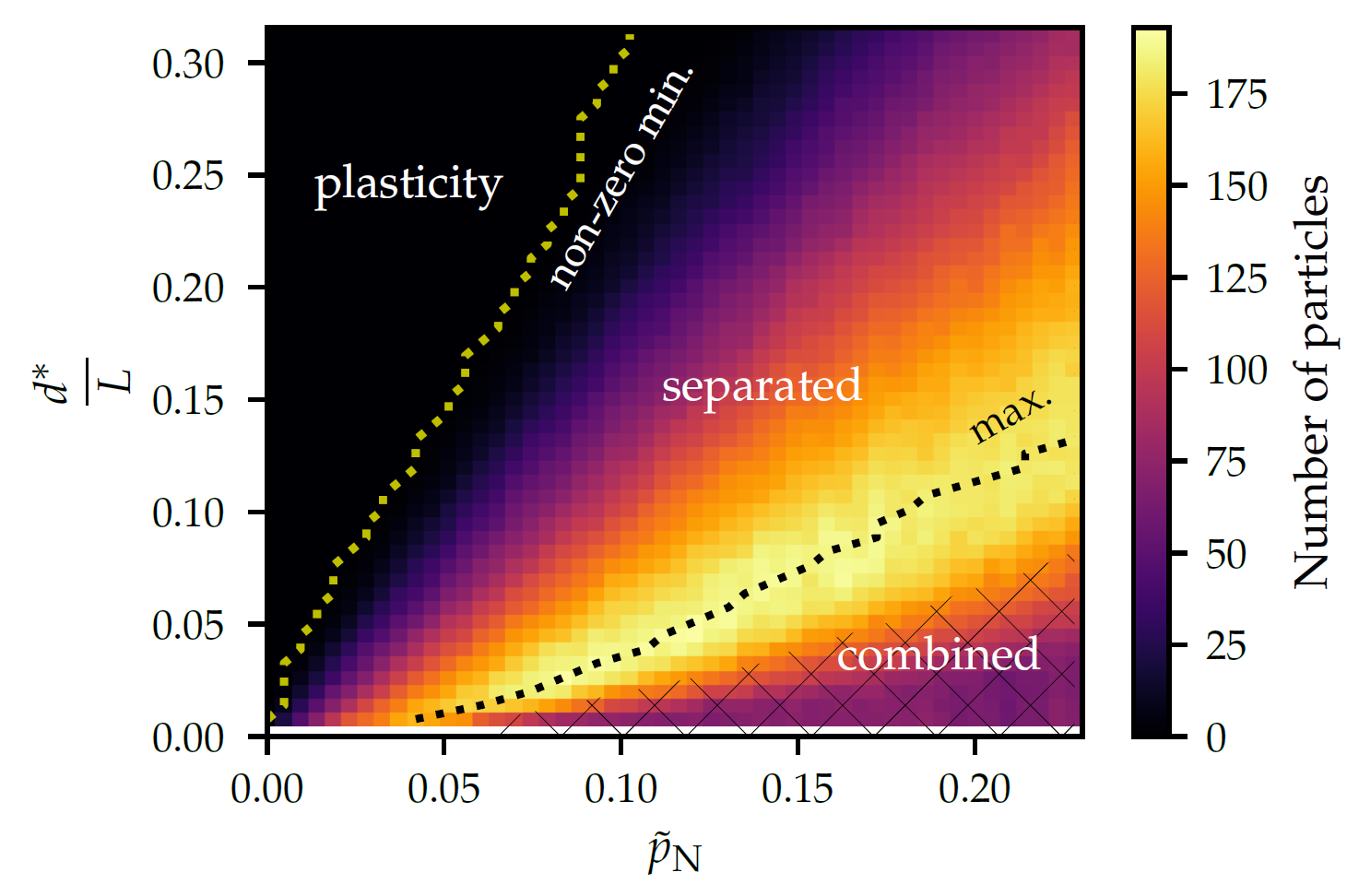
Fig. 1 – Wear map of the contact between rough surfaces, showing the number of wear particles as a function of the normal pressure \(\tilde{p}_\text{N}\) and material properties (embedded in \(d^*\)). There are clearly distinct regions, corresponding to different wear regimes
Abstract
We develop an analytical model of adhesive wear between two unlubricated rough surfaces, forming micro-contacts under normal load. The model is based on an energy balance and a crack initiation criteria. We apply the model to the problem of self-affine rough surfaces under normal load, which we solve using the boundary element method. We discuss how self-affinity of the surface roughness, and the complex morphology of the micro-contacts that emerge for a given contact pressure, challenge the definition of contact junctions. Indeed, in the context of adhesive wear, we show that elastic interactions between nearby micro-contacts can lead to wear particles whose volumes enclose the convex hull of these micro-contacts. We thereby obtain a wear map describing the instantaneous produced wear volume as a function of material properties, roughness parameters and loading conditions. Three distinct wear regimes can be identified in the wear map. In particular, the model predicts the emergence of a severe wear regime above a critical contact pressure, when interactions between micro-contacts are favored.
Keywords: adhesive wear, severe wear, self-affine surface, boundary element method